In an Enzyme Catalyzed Reaction the Reactant Is Called the
Flavonoids are one of the most important and diversified phenolic groups among products of natural origin. A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction.
Solved 29 In An Enzyme Catalyzed Reaction The Reactant Is Chegg Com
There is an image in your packet 93-96 2002 test The rate of the reaction could also be determined by.

. The following curve was generated from the data collected. If the pKa of the histidine is known to be 65 in the active site and the pH of maximum catalytic activity is 72 what is likely the primary role of histidine in the catalytic reaction. The reactants in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
Product 30- You return home to find that your baby brother has scattered his toy trains and trucks all over the floor of your room. There is an image in your packet 93-96 2002 test The rate of the reaction could also be determined by. How are reactions catalyzed.
A substance that speeds up a chemical reactionwithout being a reactantis called a catalyst. A scientist determined the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by measuring the amount of product formed over time. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction the reactant is called the.
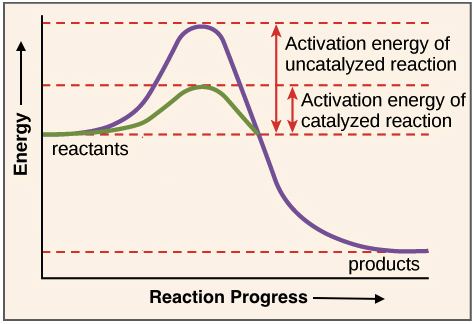
Catalysts work by lowering a reactions activation energy. A chemical reaction in which the products re-form the original reactants is called a reversible reaction. Substrate is a broadly used term but it is mainly used when talking about biochemical functions.
Terms in this set 25 An enzyme is considered an -------- because it speeds up a chemical reaction without being used up. This general characteristic is called a. In a catalyzed reaction a reactant is often called an -----.
Energy-absorbing reaction always does. THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH. Enzymes are proteins that are able to lower the activation energy for various biochemical reactions.
A histidine was determined to be the critical residue involved in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Label the following diagram that illustrates the lock-and-key model of enzyme activity. They do this by binding the reactant s known as the substrate s to an active site within the enzyme.
The lock-and-key model explains the steps involved in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction the reactant species to which the enzyme binds is called the substrate. An important property of this metabolite class is the antioxidant action.
At the active site the substrate s can form an. A substrate is a reactant that is used by an enzyme. An enzyme is specific because the shape of its -------- matches only particular reactants.
29- In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction the reactant is called the. Enzymes increase the rate of only certain reactions involving certain substances. The enzyme-catalyzed reactions involved in formation of the bicyclic clavam and carbapenem nuclei including β-amino acid and β-lactam formation have been reviewed and compared with those involved in penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthesis 05CC4251.
In the general sense substrates are the chemical species being observed during the reaction ie. What are the original substances in a chemical reaction called. This study evaluated the antioxidant and cytotoxic activities and oxidative stress of transesterification products of the flavonoid rutin catalyzed by Novozym 435.
The substrate is then converted into products by a series of steps. The following curve was generated from the data collected. The synthesis of deuterium labelled l - and d-glutamate semialdehydes their evaluation as substrates for.
The reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is called the a. Generally in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction the reactant is called the substrate which in association with the enzyme forms the product. A protein that acts as biological catalyst.
Catalyzed reactions are typically used to accelerate the rate by which a specific chemistry proceeds. As you begin to pick up the toys and put them away you realize that even though he is just a baby he has clearly. A scientist determined the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by measuring the amount of product formed over time.
In the biochemical sense this is the molecule that the enzyme is reacting with. Substrates bind to a part of an enzyme called the active site and remain bound to the enzyme. The catalysts for biochemical reactions that happen in living organisms are called enzymes.

Solved In An Enzyme Catalyzed Reaction The Reactant Species Chegg Com
Enzymes Review Article Khan Academy

Solved The Reactant Of An Enzyme Catalyzed Reaction Is Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment